Genetic polymorphisms of MnSOD modify the impacts of environmental melamine on oxidative stress and early kidney injury in calcium urolithiasis patients
Abstrcat:
Urolithiasis is a multifactorial disease that is influenced by the environment, hormones, and genes simultaneously. Among them, the impact of the emerging environmental pollutant "melamine" on urinary calculi has become a hot research topic in recent years. Our previous studies found that environmental melamine exposure increases oxidative stress and causes early kidney damage. During the normal metabolic process of the human body, reactive oxygen species (ROS) with high chemical activity will be produced, such as free radicals and peroxides. Although they can be used as intracellular message transfer molecules to regulate gene expression and cell cycle, they are also prone to oxidative reactions with other substances to cause cell damage. Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, leading to an excess of ROS. The kidney is particularly sensitive to oxidative stress, and antioxidant enzymes such as manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPX1), and catalase (CAT) are important endogenous antioxidant system, which helps protect the kidneys from oxidative stress to maintain normal function. Therefore, we hypothesized that the genetic polymorphisms of these antioxidant enzymes could modify the effects of environmental melamine exposure on oxidative stress and early renal injury in patients with calcium urolithiasis.
In this study, a total of 302 patients with calcium-containing urolithiasis were enrolled, and five genetic polymorphisms of antioxidant enzyme genes, including MnSOD (rs4880 and rs5746136), GPX1 (rs1800668), and CAT (rs1001179 and rs769217) were investigated. Those genetic polymorphisms had been found to associate with several kidney diseases and were selected to evalute their relationships with indicators of oxidative stress (malondialdehyde, MDA and 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, 8-OHdG) and renal tubular damage (N-acetylglucosamine, NAG) in urine.
The results showed that in the rs4880 polymorphism of MnSOD gene, subjects carrying the T allele have increased 1.80-fold risk of higher oxidative stress (MDA value >50%) than those carrying the C allele; while in another rs5746136 polymorphism of MnSOD gene, subjects carrying the G allele have increased 1.36-fold risk of higher renal tubular damage (NAG value>50%) than those carrying the A allele.
The results in further multivariate correction model showed that the effects of the above two polymorphisms of MnSOD genes on the indicators of oxidative stress and renal tubular damage were significantly increased in subjects with higher melamine exposure.
In conclusion, this study found that two polymorphisms (rs4880 and rs5746136) of the MnSOD gene could modify the risk of oxidative stress and renal tubular injury in patients with calcium urolithiasis, respectively. This effect was more pronounced in groups with higher melamine exposure. This result confirmed that polymorphisms of antioxidant enzyme genes could regulate the risk of oxidative stress and early kidney damage caused by environmental melamine exposure in humans. Therefore, when establishing the daily tolerance intake of melamine for humans in the future, the genetic polymorphisms of these antioxidant enzymes may need to be considered, especially for susceptible groups such as patients with calcium urolithiasis.
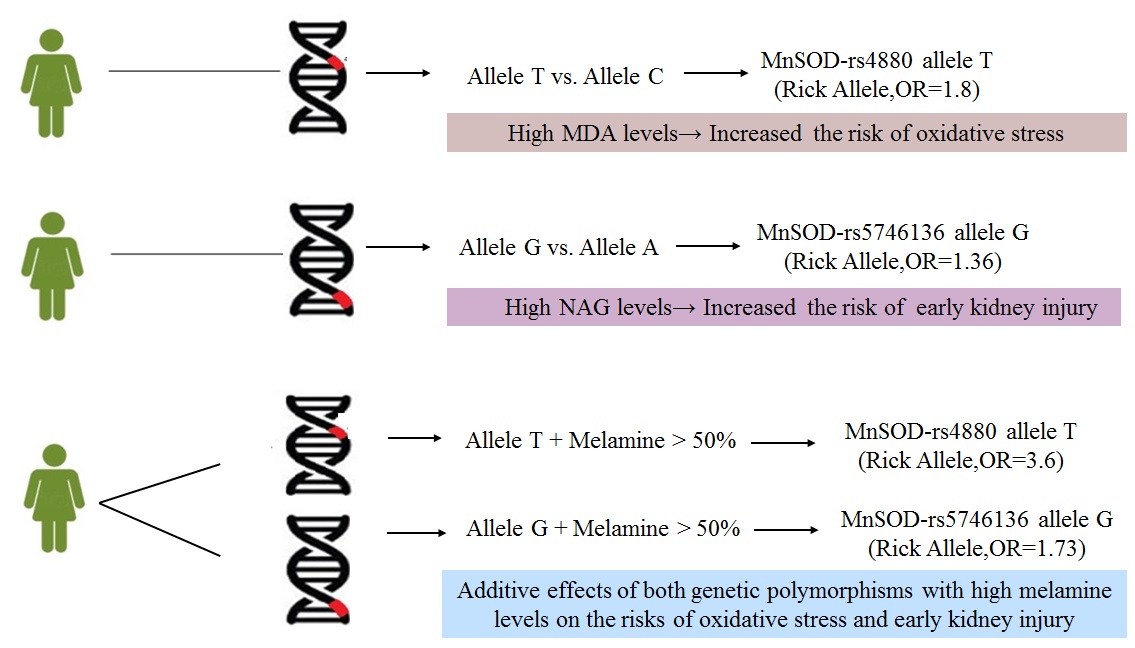
Schematic diagram of the genetic polymorphisms of manganese superoxide dismutase gene could modify the risk of oxidative stress and early kidney injury in humans.
Key Points:
- This study found that the genetic polymorphisms of antioxidant enzyme "manganese superoxide dismutase" could regulate the impact of melamine exposure in the environment on oxidative stress and early kidney damage in adult patients with calcium urolithiasis.
- The results of this study will help to establish a foundation for future research on susceptibility genes and underlying mechanisms for the impact of environmental melamine exposure on human health.
- The early kidney damage and other human effects of melamine on high-risk and susceptible groups should still be kept with attention and evaluation that should not be ignored.
More Information:
Liu CC, Wu CF, Lee YC, Huang TY, Huang ST, Wang HS, Jhan JH, Huang SP, Li CC, Juan YS, Hsieh TJ, Tsai YC, Chen CC, Wu MT*. Genetic Polymorphisms of MnSOD Modify the Impacts of Environmental Melamine on Oxidative Stress and Early Kidney Injury in Calcium Urolithiasis Patients. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;11(1):152. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010152. (SCIE, IF2021: 7.675, 4/63=6.35% in CHEMISTRY, MEDICINAL)