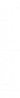【Research Highlights】Innovative Analytical Techniques for Identifying Metabolites of the UV Filter Homosalate through UPLC-MS: Environmental and Health Implications (Assistant Professor Yi-Shiou Chiou)
2025 / 12 Assistant Professor Yi-Shiou Chiou (Master Degree Program in Toxicology, College of Pharmacy)
Homosalate: A Common but Discussable Sunscreen Component
In modern life, sunscreen products have become an essential part of daily skincare, and the chemical sunscreen components play a crucial role in protecting the skin. Homosalate (HMS) is currently a widely used UVB absorber in many commercially available sunscreen lotions, skin care products, and cosmetics. Its main function is to reduce skin damage caused by ultraviolet rays. However, recent toxicological studies have indicated that Homosalate may have estrogenic activity and is related to anti-androgenic effects, increasing the discussion on its hormonal interference risks.
An Overview of the Metabolism of Homosalate Sunscreen Component
As people's awareness of the safety of chemical components gradually increases, the health and environmental risks of Homosalate have also begun to attract attention. Currently, Homosalate has been detected in river waters, coastal waters, sediments, indoor dust, and even seafood in multiple research units worldwide; it has also been found in human samples in urine and breast milk. These data indicate that Homosalate has a certain potential for accumulation and circulation regardless of environmental exposure or skin absorption. Therefore, understanding the metabolic pathway of Homosalate in the body has become an important topic in chemical exposure assessment and product safety management.
The Objectives and Main Contributions of This Study
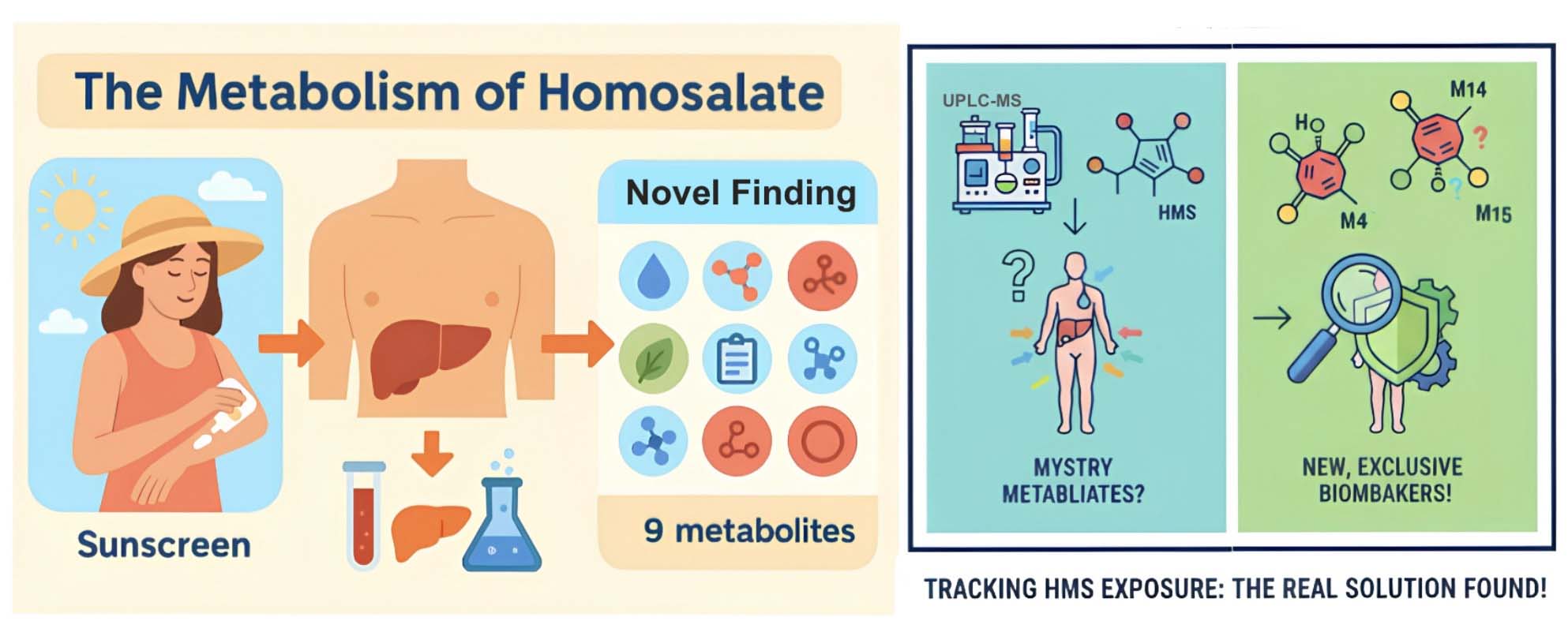
Regarding the core question of "Which compounds are formed by Homosalate in the human liver?", we used UPLC-MS combined with isotope labeling and three complementary metabolite data processing strategies to establish a technical process that can comprehensively analyze metabolites. Through these methods, we successfully identified nine metabolites of Homosalate, including those known in the literature and new metabolites identified for the first time in this study. This result not only significantly enriches the understanding of Homosalate metabolism in the past but also lays an important foundation for future health risk assessment, environmental exposure monitoring, and toxicological research.
Application and Highlights:
- The unique structural-specific metabolites M14 and M15 of Homosalate were identified for the first time.
- Salicylic acid is the main metabolite of Homosalate, but it cannot be used as an exposure indicator.
- The newly discovered metabolites M14 and M15 can be regarded as potential exposure biomarkers.
More Information:
Chiou YS#, Liu CH#, Wu ZH, Tseng MF, Chang SC, Chang YW, Huang CY*, Shih CL*. Innovative analytical techniques for identifying metabolites of the UV filter homosalate through UPLC–MS: Environmental and health implications. Environmental Pollution, 2025, 386, 127161. (SCIE, IF2024: 7.3, 47/376=12.30% in ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES)
Team Member:
Yi-Shiou Chiou, Chia-Lung Shih, Ji-Rui Yang, Min-Feng Tseng, Shin-Yu Yao
Introduction of Research Team:
Professor Yi-Shiou Chiou research team focuses on environmental toxicology, metabolomics and precision health. By integrating high-resolution mass spectrometry, multi-omics, and cell/animal/clinical models, we are dedicated to uncovering the effects of environmental hormone exposure on health and developing innovative strategies with clinical and industrial value.